Revenue Sharing Case Study: Mineral Revenue Sharing in Peru
In 2013, Peru was the world’s second-largest producer of copper and silver, and the sixth-largest producer of gold. The country also holds significant reserves of coal, iron ore, tin, sulphur and zinc. In 2014, the contribution of the mining sector to Peru’s GDP was 12 percent and minerals made up 52 percent of total exports.
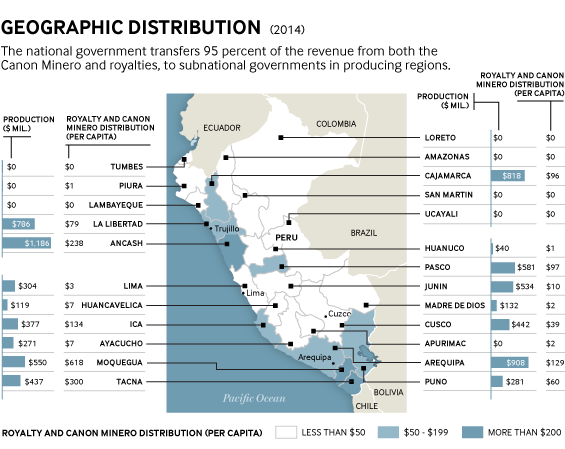
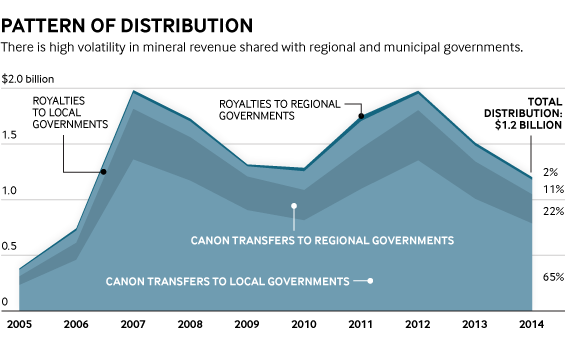
This case study and related infographic provide an overview of natural resource-related intergovernmental transfers in Peru—that is, the revenue that the Peruvian national government earns from extraction and then redistributes to subnational governments.
The case study outlines fiscal decentralization and the evolution of revenue sharing, and provides an overview of how resource revenues are collected and then shared with subnational governments, within the wider intergovernmental transfer system in Peru. Where there is sufficient information, the study highlights the statutory earmarks of revenue and the level of transparency and effectiveness of the revenue sharing system. It is primarily intended to inform policy debates on revenue sharing in Peru and other countries. It may also be of interest to researchers further exploring key issues related to this topic. It forms part of a broader set of case studies on revenue sharing.